Offshoring, Nearshoring, Onshoring & Outsourcing
Veröffentlicht von InterVenture am Mai 14, 2019
Characteristics and Differences
Near – Off – Out – On, first of all we need to keep track. Four terms whose meanings are similar, but explain different situations. Offshoring, Nearshoring, Onshoring and Outsourcing all refer to the process of a company transferring different segments or services of their business to another company for reasons such as reduction of costs.
Outsourcing
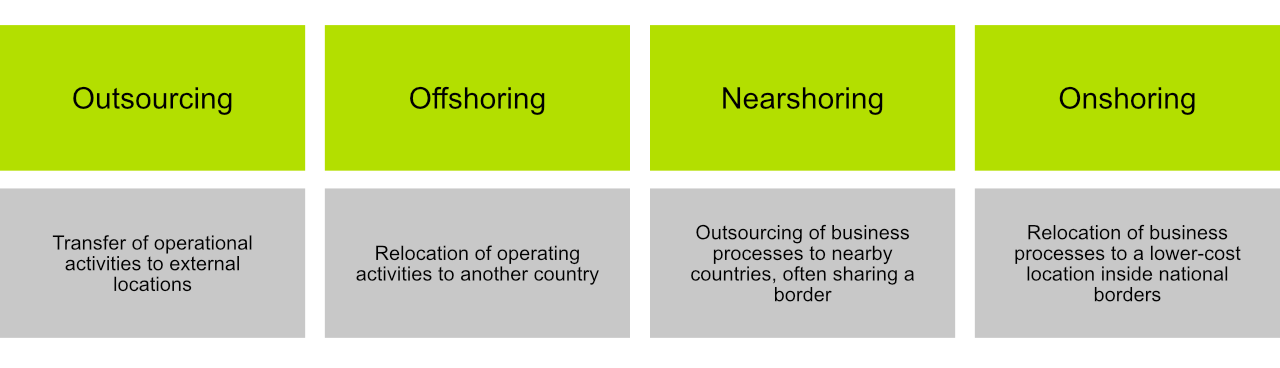
Outsourcing involves the transfer of operational activities of the value-based suppliers. The aim is to shorten the supply chain and a reduction in services supplied internally within the company can be achieved.
Outsourcing is usually operated with the aim of saving costs. Especially development, production and fixed costs can be reduced significantly. For example, if a company is more focused on strengthening its creativity, outsourcing parts of its production process to a company who specialises in this sector could allow the business to minimise additional costs and to reinvest its savings. As a consequence, the company can improve its market position, on both strategic and functional levels.
A business removing a manufacturing department could move its factory elsewhere or utilise another company’s instead. This method is also often applied in the service sector.
Offshoring
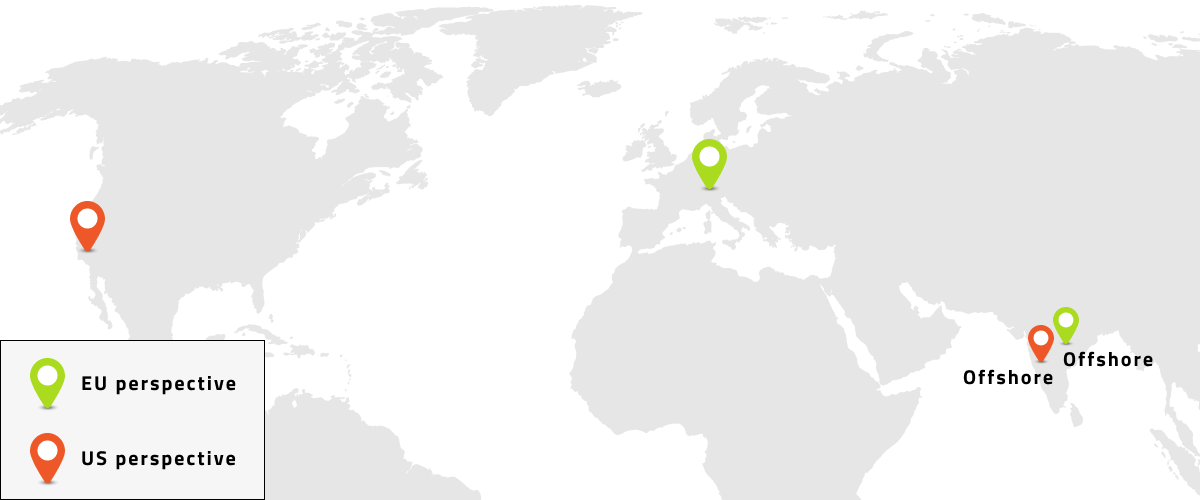
With Offshoring, the operating activities are relocated to another country, and the geographical location is irrelevant. Offshoring can be divided into two subdivisions, namely Nearshoring (neighbouring countries with or without a shared border) and Farshoring (distant countries e.g. countries in East Asia).
Offshoring is often employed to reduce the personnel costs of a company. However, its success is subject to several requirements – one of which regards communication. Strong internet connections are also particularly important for all peripheral devices to allow for effective communication. If IT companies are linguistically and technically focused on highly qualified employees abroad, they usually choose Nearshoring as an alternative due to same spoken language, for example.
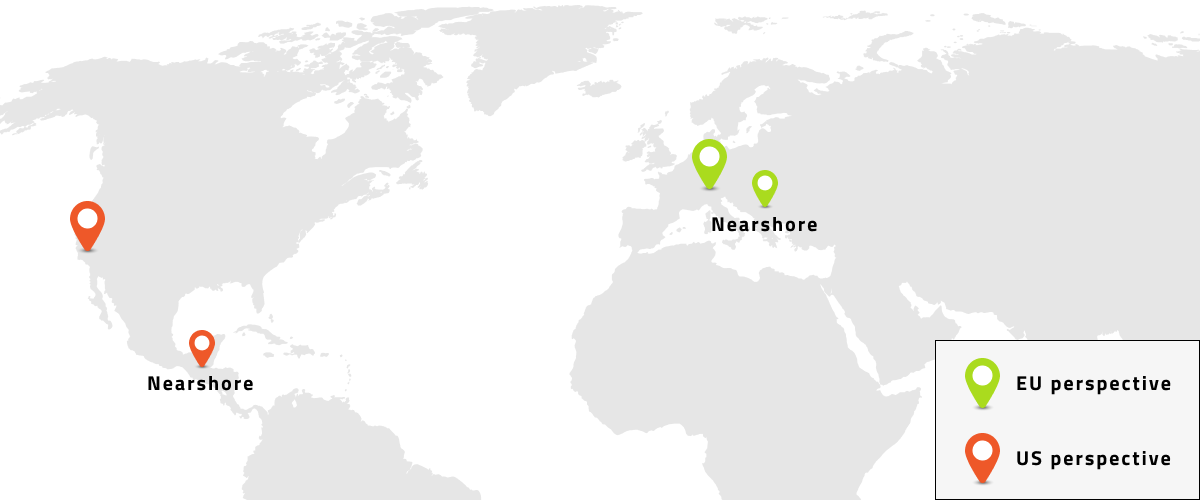
Nearshoring
Nearshoring is the outsourcing of business processes, especially information technology processes, to companies in a nearby country, often sharing a border with the target country. Therefore, it is the opposite of Farshoring and can be seen as a special form of Offshoring.
For a company based in Germany, typical Nearshoring locations include the following:
- Poland
- the Czech Republic
- and Serbia.
Nearshoring offers optimal solutions for companies that want to outsource processes in order to maximize business efficiency but reduce the barriers of traditional offshoring. Compared to offshoring, the benefits are, for example, no or little time shift as well as cultural differences, easy communication due to good language skills and fast but also cost-effective travel.
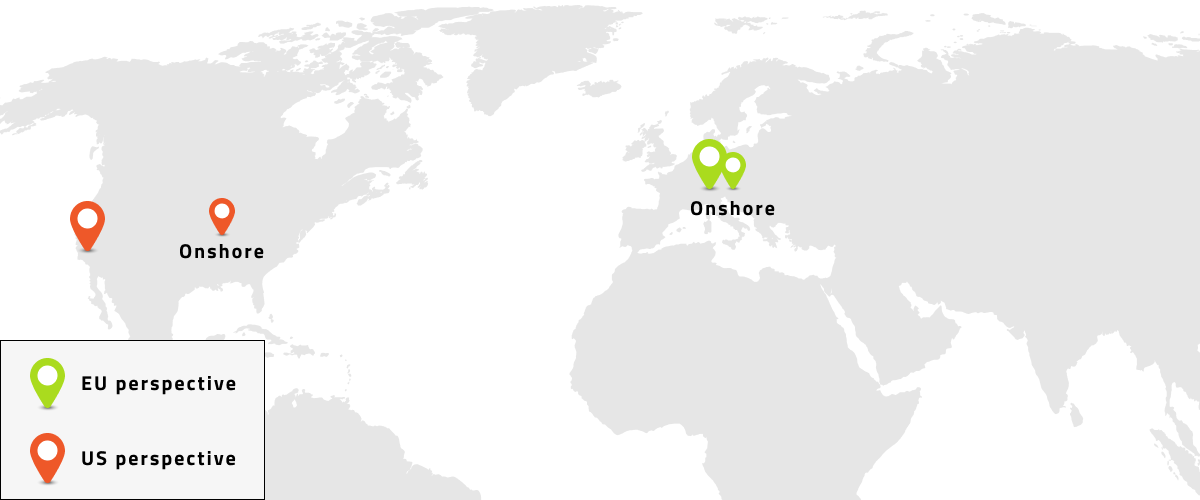
Onshoring
Onshoring is the exact opposite of Offshoring, it refers to the relocation of business processes to a lower-cost location inside the national borders. Functions and processes are often located to a nearby location, this is often the case with big clients, as close proximity may be a condition of the working agreement. A typical example could be suppliers of the automotive industry. Working in close proximity (often directly next to the factory premises of their customers) allows a business to provide the quickest possible service, one that is tailored to suit their market needs and therefore supply customers based on the just-in-time principle.
Onshoring improves the cost structure considerably and allows great flexibility within organisations. Furthermore, the coordination and communication of production is more effective and efficient.
What to choose?
Obviously, each of these variants of outsourcing has advantages and drawbacks. Hence, a universal recommendation is not possible. It always depends on different factors, such as set goals, available resources or certain other requirements. While Farshoring might offer the best solution for saving personnel expenses, it should also be noted that cultural differences and operating in different time zones might cause a whole new and unexpected range of costs.
On the other hand, the reasons for choosing a Nearshoring solution include communication and business trips. This means that in the long run, choosing slightly higher wages might be a better solution, as having to coordinate another team on the other side of the world might offset the savings of outsourcing to a low-wage country or even surpass it.